一个优秀的后端,是不会相信任何传入的参数的
要做到这一点,以前我们是写大量的判断代码来验证数据的格式
在开发中,我们实际不这么干,我们使用Hibernate Validator来进行参数校验
它实现了JSR 303规范,使我们的代码的健壮性大大提高
先列出一些常用注解
| 约束注解 |
详细信息 |
@Null |
被注释的元素必须为 null |
@NotNull |
被注释的元素必须不为 null |
@AssertTrue |
被注释的元素必须为 true |
@AssertFalse |
被注释的元素必须为 false |
@Min(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
@Max(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
@DecimalMin(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
@DecimalMax(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
@Size(max, min) |
被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
@Digits (integer, fraction) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
@Past |
被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
@Future |
被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
@Pattern(value) |
被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
@Email |
被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址 |
@Length |
被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
@NotEmpty |
被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
@Range |
被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
使用方式也很简单,springboot引入依赖就可以使用了
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
公司常用的方式是用注解方式,关于另一种方式和spring实现方式之后的博客会写
我们之前写的springboot项目中用的aop方式实现参数校验,这里我先给他废弃掉
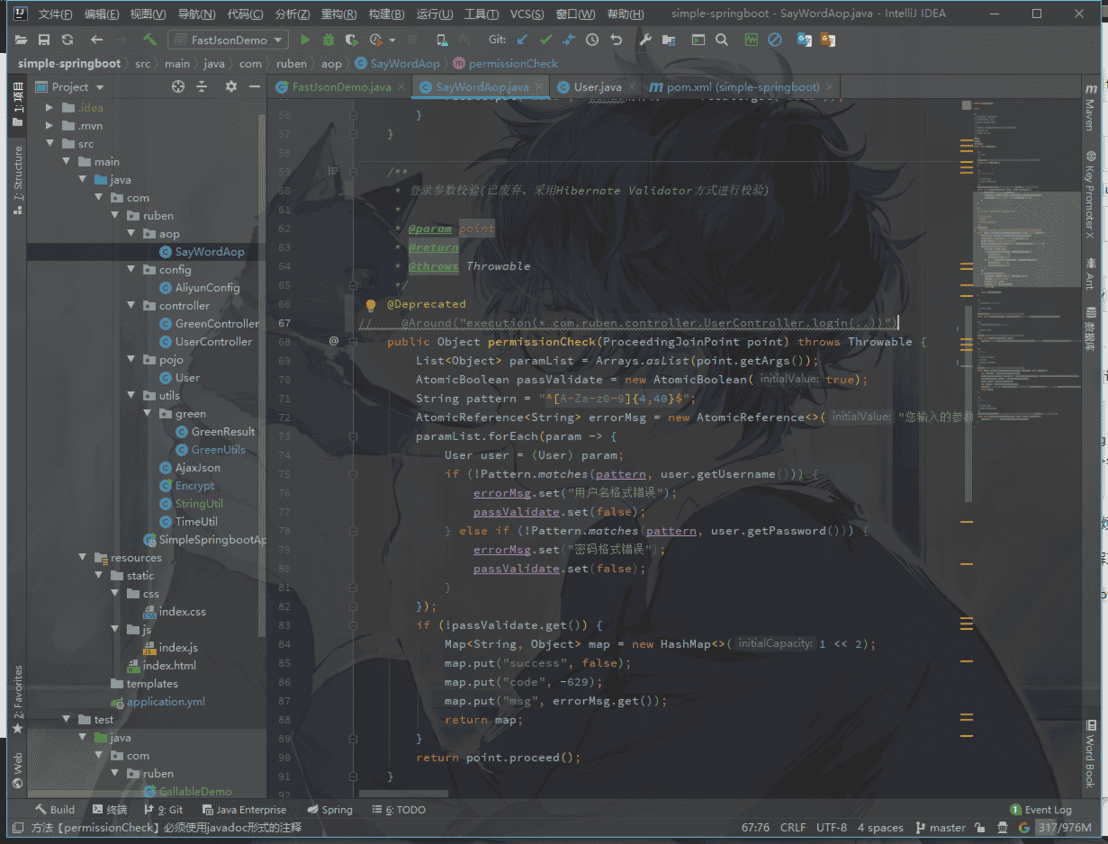
然后校验已经关闭了
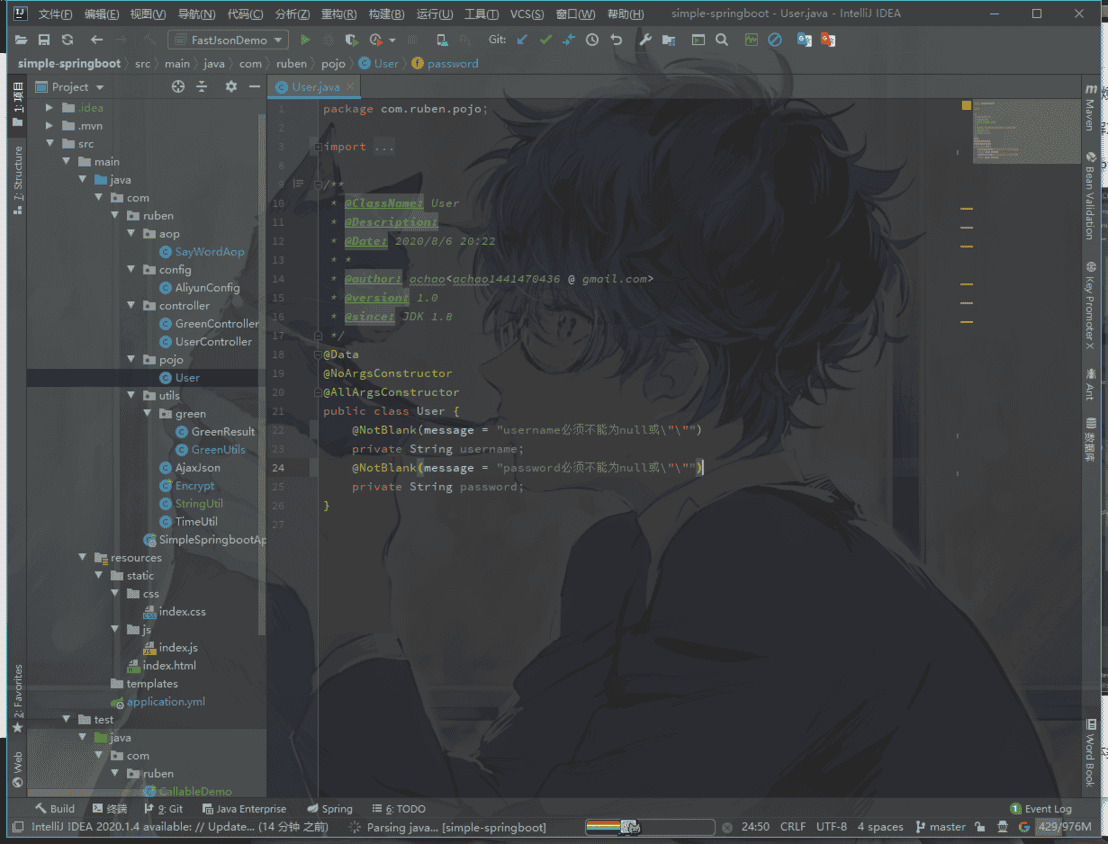
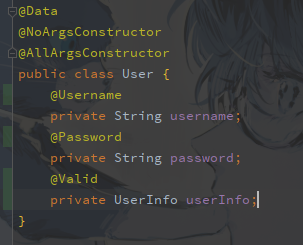
我们首先去给接参的实体类加上注解
然后在接口上加@Valid注解
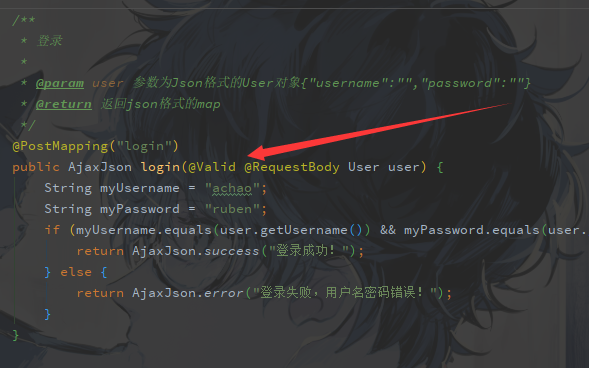
这个时候我们启动项目发现,已经成功校验了,如果我们参数格式错误,会抛出一个MethodArgumentNotValidException
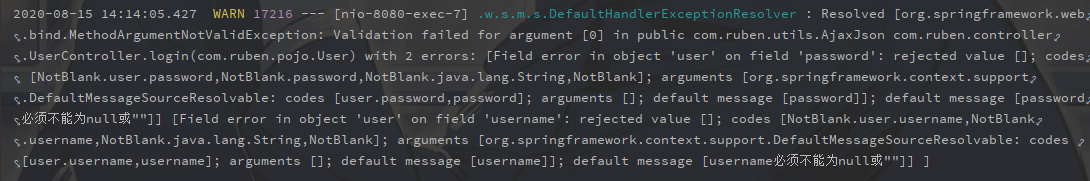
这时候我们就只需要在全局异常处理器进行捕获,返回提示就可以了,全局异常处理器怎么写呢?之后的博客也会提到,在此之前可以试着自己动手写一下
如果提供的原生的注解不满足我们的需要,我们可以自定义
先点进去注解内部
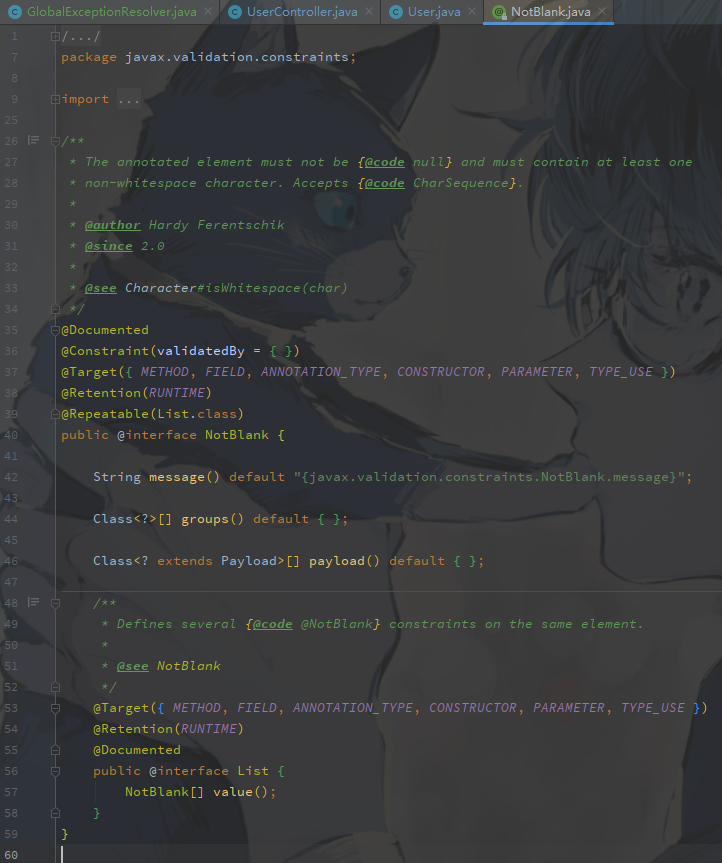
我们照着写一个
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| package com.ruben.validator;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
import javax.validation.ReportAsSingleViolation;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
@NotBlank
@Documented
@Pattern(regexp = "^[A-Za-z0-9]{8,16}$")
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = {})
@ReportAsSingleViolation
@Target({METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE})
public @interface Username {
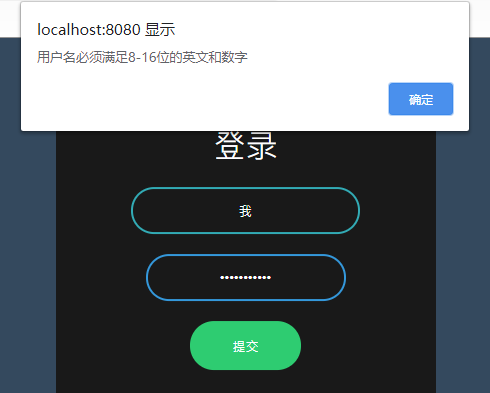
String message() default "用户名必须满足8-16位的英文和数字";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
|
换成我们的Username
可以看到生效了
当然,我这里是做了全局异常处理才能达到这样的效果的,不然还是控制台抛异常。。。
这时候可能有小伙伴问了,如果我想自定义规则怎么办呢?
那么我们密码就来实现一波自定义规则
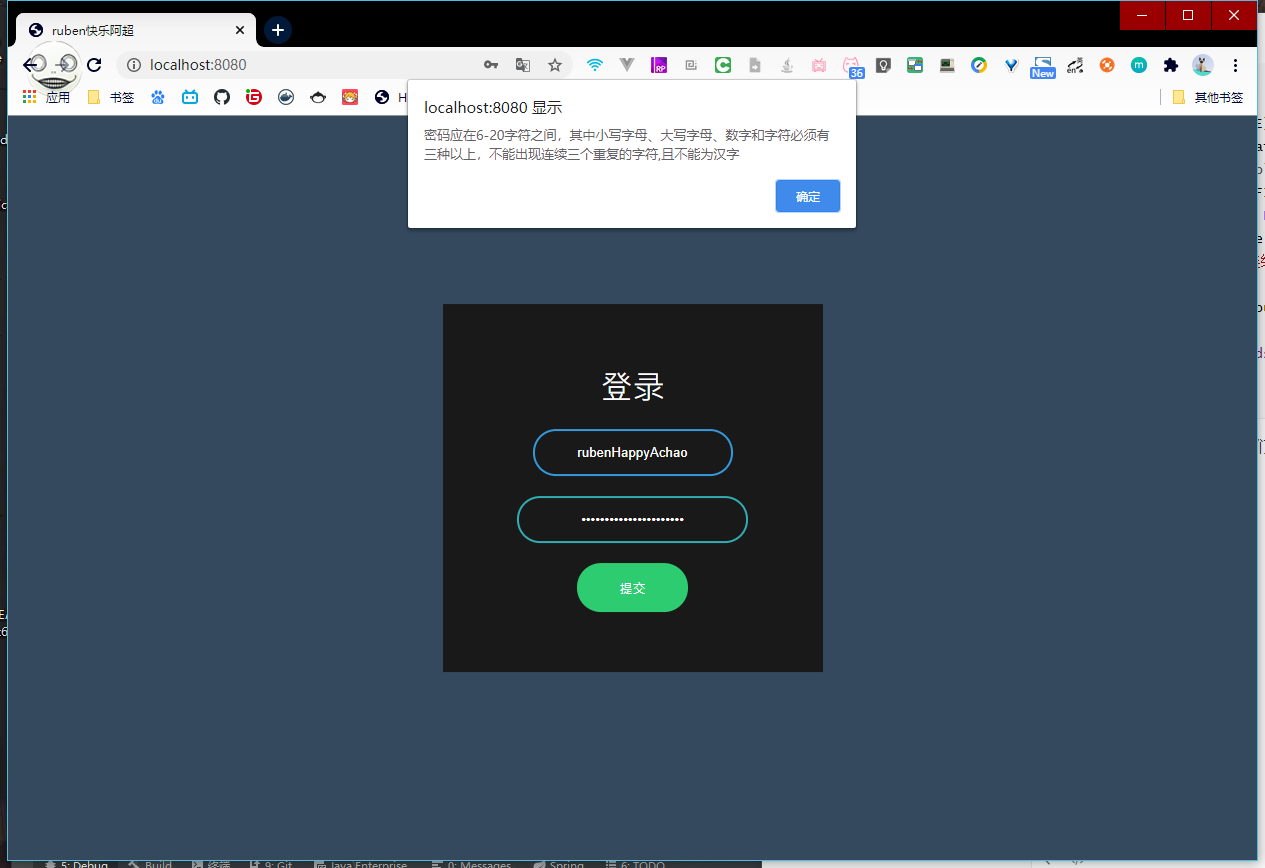
比如整个简单的密码应在6-20字符之间,其中小写字母、大写字母、数字和字符必须有三种以上,不能出现连续三个重复的字符,且不能为汉字
首先创建一个校验类,继承ConstraintValidator<?,?>
然后重写方法写好判断,return 一个boolean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
| package com.ruben.validator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class PasswordValidator implements ConstraintValidator<Password, String> {
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if (value.length() <= 6 || value.length() >= 20) {
return false;
}
if (value.contains(" ")) {
return false;
}
boolean hasUpperCase = false;
boolean hasLowerCase = false;
boolean hasNumber = false;
boolean hasCharacter = false;
String upperCaseRegexp = "^[A-Z]+$";
String lowerCaseRegexp = "^[a-z]+$";
String numberRegexp = "^[0-9]*$";
Pattern upperCasePattern = Pattern.compile(upperCaseRegexp);
Pattern lowerCasePattern = Pattern.compile(lowerCaseRegexp);
Pattern numberPattern = Pattern.compile(numberRegexp);
int countRepeat = 0;
char[] chars = value.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (i != chars.length - 1 && chars[i] == chars[i + 1]) {
countRepeat++;
}
if (countRepeat == 3) {
return false;
}
String singleChar = String.valueOf(chars[i]);
String chineseRegexp = "^[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]*$";
Pattern chinesePattern = Pattern.compile(chineseRegexp);
if (chinesePattern.matcher(singleChar).matches()) {
return false;
}
if (upperCasePattern.matcher(singleChar).matches()) {
hasUpperCase = true;
} else if (lowerCasePattern.matcher(singleChar).matches()) {
hasLowerCase = true;
} else if (numberPattern.matcher(singleChar).matches()) {
hasNumber = true;
} else {
hasCharacter = true;
}
}
int countMatches = 0;
if (hasUpperCase) {
countMatches++;
}
if (hasLowerCase) {
countMatches++;
}
if (hasNumber) {
countMatches++;
}
if (hasCharacter) {
countMatches++;
}
return countMatches >= 3;
}
}
|
然后再自定义我们的注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package com.ruben.validator;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
import javax.validation.ReportAsSingleViolation;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
@NotBlank
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = PasswordValidator.class)
@ReportAsSingleViolation
@Target({METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE})
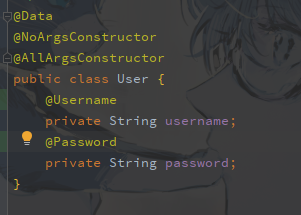
public @interface Password {
String message() default "密码应在6-20字符之间,其中小写字母、大写字母、数字和字符必须有三种以上,不能出现连续三个重复的字符,且不能为汉字";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
|
然后在我们的参数上加上我们自定义的注解
重启,测试,发现测试通过
如果是枚举的话,也得使用这种自定义的方式去做校验
这里提一下,如果是嵌套的话,需要在嵌套的对象上加@Valid注解才能生效
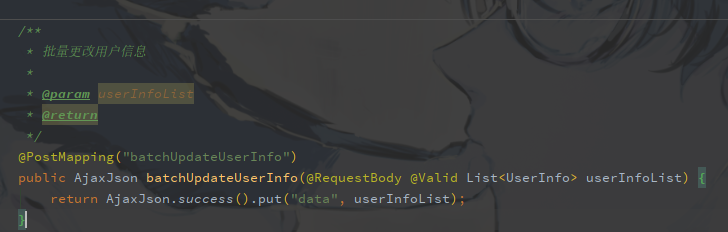
还有如果接参是List,要在List前边加@Valid
今天博客就到这里啦,明天再见










